Descripción
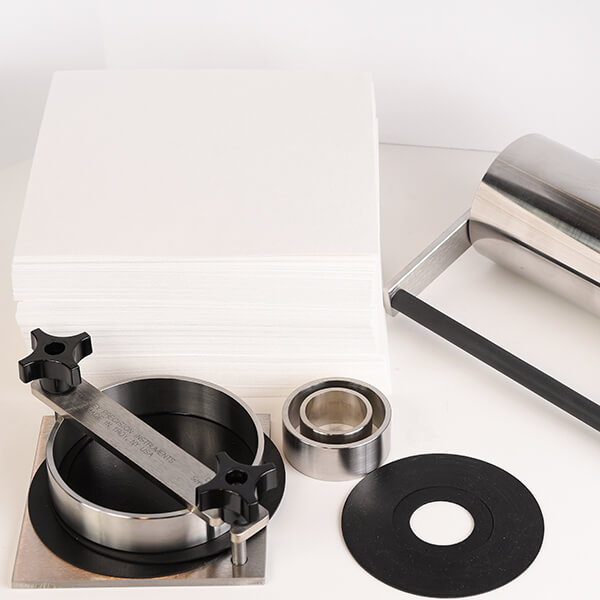
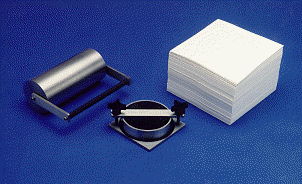
Gurley™ Cobb Sizing Testers have been manufactured by Gurley for over a half-century Represent an economical and practical means of determining liquid absorptiveness or resilience of treated and untreated papers, boards, fabrics and other sheet materials. The complete kit consists of the Gurley- Cobb test apparatus, its 10-kg roller and a supply of blotting paper. The roller method is recommended to insure better consistency and reliability that can be obtained by manual blotting or rubbing the specimen.
| Kit 4180DN Includes: 100, 25 & 10 cm2 rings CX00856 roller AX05022 blotting paper (250 sheets) |
Kit 4180CN Includes: Gurley Cobb tester with 100cm2 ring CX00856 roller AX05022 blotting paper (250 sheets) |
Kit 4180CB Includes: Gurley Cobb tester with 25 cm2 ring CX00856 roller AX05022 blotting paper (250 sheets) |
Kit 4180CC Includes: Gurley Cobb tester with 10 cm2 ring CX00856 roller AX05022 blotting paper (250 sheets) |
|
4180BN |
4180AN 100cm2 ring |
4180AA 25 cm2 ring |
4180AD 10 cm2 ring |
|
CX00856 |
AX05022 |
AX05023 Blotting Paper (Case of 2,250 sheets |
Industry Standards: ISO 535 & TAPPI T441
Purpose of Test
Water absorptiveness of paper board or other materials is a function of various characteristics such as sizing, porosity, etc. The Gurley-Cobb sizing test can be used to test absorption or resistance to absorption of water, oil and other liquids.
Principle
This procedure determines the quantity of water absorbed by a sample of paper or other sheet material in a specified time and under standardized conditions. Other liquids such as ink, beverages, oil and water based solutions may be used instead of water. The standard area is one hundred square centimeters (cm2), into which 100cc of liquid are poured to reach a specific height of 1 cm. For smaller samples, proportionately smaller areas (25 and 10 cm2) can be tested.
Description
The Gurley-Cobb Sizing Tester consists of a hollow metal cylinder or ring (100, 25 or 10 cm2 inside area); a metal base plate with a clamping device to hold the ring against the sample and a Neoprene mat. Neoprene gaskets also are supplied to seal off the cylinder when testing uneven materials where an ungasketed seal is difficult to maintain. A critical component of this test is a solid stainless steel roller having a smooth face 20cm wide and weighing 10.0+ 0.5kg.Also required for the test are a 100ml graduated cylinder, a balance with sensitivity of 0.01g or better, blotting paper and a timer or stopwatch.
Use of the Tester
In advance of conditioning, cut sample to approximately 12.5 x 12.5cm. After conditioning, weigh sample, place it on the Neoprene mat and clamp the appropriate (typically 100 sq. cm.) cylinder upon it by locking crossbar in place and tightening two knobs. If sample material is textured, place the gasket between the sample and cylinder, carefully aligning the inner edges of each. Pour in the test liquid (100ml for 100 sq. cm. cylinder, proportionately less for others). Start timing the test immediately when beginning to pour the liquid. Test duration is generally 120 seconds. More absorbent materials may be tested for shorter periods (60 seconds) while less absorbent materials may be tested for as long as eighteen hours. At fifteen seconds before the expiration of the predetermined test period, pour the liquid quickly from the cylinder, using care in not dropping any on the untreated (outside) portion of the specimen. Promptly loosen knobs and swing crossbar out of the way while holding ring down against specimen. Quickly but carefully remove the ring and place specimen with wetted side up on a sheet of blotting paper.
Use of Roller
At exactly the end of the predetermined test period, place a second sheet of blotting paper on top of the sample and remove the surplus water or other liquid by moving the hand roller once forward and once back over the pad. Care should be taken not to exert downward force on the roller. Alternative methods of blotting, such as rubbing with a cloth, are not recommended as the amount of blotting is uneven and will affect the outcome. Fold the specimen after removing it from between the blotter sheets and reweigh to the nearest 0.01g.Subtract the conditioned weight of the specimen from its final weight and multiply the gain in grams by 100 to obtain the weight of liquid absorbed in grams per square meter. For the 25 or 10 sq. cm. cylinders, multiply by 400 or 1000 respectively, to obtain grams per square meter.